It’s that time of the year again as we walk you through the FDA new drug approvals over the past twelve months. We break down the approvals by the numbers and highlight each small molecule and biologic therapy approved. We provide a short description of how they work, their competitors and pivotal clinical trials for all 37 new medicines entering the market in 2022.
There were 37 new drugs approved by the FDA in 2022, compared to 50 in 2021. 22 were small molecules, and 15 were biologic drug approvals. Oncology (anticancer) drugs led the pack with 11 approvals, followed closely by autoimmune therapies with 7 approvals. 23 of the 37 approved drugs are considered first-in-class therapies.
Note: this resource will continue to be updated and expanded through 2022/2023 as more information (new approvals, sales numbers, phase 4 trials, etc.) becomes available. Feel free to bookmark this page to stay up to date!
Below is a table showing approved drugs, the pharmaceutical company that developed them, their approved therapeutic use and drug class, along with FDA special designations (if any).
| No. | Drug Brand Name | Drug Generic Name | Approval Date (MM-DD) | Drug Type | Company | Therapeutic Use | Drug Target Class | FDA Designations* | First-in-Class? (Y/N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quviviq | daridorexant | 01-07 | Small molecule | Idorsia Pharmaceuticals | Insomnia | Central Nervous System | 0 | N |
| 2 | Cibinqo | abrocitinib | 01-14 | Small molecule | Pfizer | Eczema | Autoimmune (Skin) | 0 | N |
| 3 | Kimmtrak | tebentafusp | 01-25 | Biologic | Immunocore | Eye melanoma | Oncology (Eye) | 3 (BT, OD, PR) | Y |
| 4 | Vabysmo | faricimab | 01-28 | Biologic | Roche | Macular degeneration | Ophthalmology | 0 | Y |
| 5 | Enjaymo | sutimlimab | 02-04 | Biologic | Sanofi | Cold agglutinin disease | Autoimmune (Blood) | 3 (BT, OD, PR) | Y |
| 6 | Pyrukynd | mitapivat | 02-17 | Small molecule | Agios Pharmaceuticals | Hemolytic anemia | Others (Blood) | 2 (OD, PR) | Y |
| 7 | Vonjo | pacritinib | 02-28 | Small molecule | CTI BioPharma | Myelofibrosis | Oncology (Blood) | 4 (AA, FT, OD, PR) | Y |
| 8 | Ztalmy | ganoxolone | 03-18 | Small molecule | Marinus Pharmaceuticals | Seizures | Central Nervous System | 3 (OD, PR, VG) | Y |
| 9 | Opdualag | nivolumab and relatlimab | 03-18 | Biologic | Bristol Myers Squibb | Melanoma | Oncology (Skin) | 3 (FT, OD, PR) | N |
| 10 | Pluvicto | lutetium vipivotide tetraxetan | 03-23 | Small molecule | Novartis | Prostate cancer | Oncology (Prostate) | 2 (BT, PR) | Y |
| 11 | Vivjoa | oteseconazole | 04-26 | Small molecule | Mycovia Pharmaceuticals | Vulvovaginal candidiasis | Infectious Disease | 1 (PR) | N |
| 12 | Camzyos | mavacamten | 04-28 | Small molecule | Bristol Myers Squibb | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Cardiovascular | 0 | Y |
| 13 | Voquezna | vonoprazan and amoxicillin and clarithromycin | 05-03 | Small molecule | Phathom Pharmaceuticals | Helicobacter pylori infection | Infectious Disease | 1 (PR) | N |
| 14 | Mounjaro | tirzepatide | 05-13 | Small molecule | Eli Lilly | Blood sugar control | Autoimmune (Diabetes) | 1 (PR) | Y |
| 15 | Vtama | tapinarof | 05-23 | Small molecule | Dermavant Sciences | Plaque psoriasis | Autoimmune (Skin) | 0 | Y |
| 16 | Amvuttra | vutrisiran | 06-13 | Small molecule | Alnylam Pharmaceuticals | Amyloidosis | Others (Liver) | 2 (FT, OD) | N |
| 17 | Xenpozyme | olipudase alfa | 08-31 | Biologic | Sanofi | Acid sphingomyelinase deficiency | Others | 5 (BT, FT, OD, PR, VG) | Y |
| 18 | Spevigo | spesolimab | 09-01 | Biologic | Boehringer Ingelheim | Pustular psoriasis | Autoimmune (Skin) | 2 (BT, OD) | Y |
| 19 | Daxxify | daxibotulinum toxin A | 09-07 | Biologic | Revance Therapeutics | Frown lines (cosmetic) | Others | 0 | N |
| 20 | Sotyktu | deucravacitinib | 09-09 | Small molecule | Bristol Myers Squibb | Plaque psoriasis | Autoimmune (Skin) | 0 | Y |
| 21 | Rolvedon | eflapegrastim | 09-09 | Biologic | Spectrum Pharmaceuticals | Reduce infection in chemotherapy patients | Infectious Disease | 0 | N |
| 22 | Terlivaz | terlipressin | 09-14 | Small molecule | Mallinckrodt | Improve kidney function | Others (Kidney) | 3 (FT, OD, PR) | Y |
| 23 | Elucirem | gadopiclenol | 09-21 | Small molecule | Guerbet | MRI contrast agent | Others (Medical Imaging) | 1 (PR) | N |
| 24 | Omlonti | omidenepag | 09-22 | Small molecule | Santen Pharmaceutical | Glaucoma | Ophthalmology | 0 | Y |
| 25 | Relyvrio | sodium phenylbutyrate and taurursodiol | 09-29 | Small molecule | Amylyx Pharmaceuticals | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | Central Nervous System | 2 (OD, PR) | Y |
| 26 | Lytgobi | futibatinib | 09-30 | Small molecule | Taiho Oncology | Bile duct cancer | Oncology (Gastrointestinal) | 4 (AA, BT, OD, PR) | N |
| 27 | Imjudo | tremelimumab | 10-21 | Biologic | AstraZeneca | Liver cancer | Oncology (Liver) | 0 | N |
| 28 | Tecvayli | teclistamab | 10-25 | Biologic | Johnson & Johnson | Multiple myeloma | Oncology (Blood) | 4 (AA, BT, OD, PR) | Y |
| 29 | Elahere | mirvetuximab soravtansine | 11-14 | Biologic | ImmunoGen | Ovarian cancer | Oncology (Ovarian) | 2 (AA, PR) | Y |
| 30 | Tzield | teplizumab | 11-18 | Biologic | Provention Bio | Type 1 Diabetes | Autoimmune (Diabetes) | 2 (BT, PR) | Y |
| 31 | Rezlidhia | olutasidenib | 12-01 | Small molecule | Rigel Pharmaceuticals | Acute myeloid leukemia | Oncology (Blood) | 0 | N |
| 32 | Krazati | adagrasib | 12-12 | Small molecule | Mirati Therapeutics | Non-small cell lung cancer | Oncology (Lungs) | 4 (AA, BT, FT, OD) | N |
| 33 | Sunlenca | lenacapavir | 12-22 | Small molecule | Gilead Sciences | HIV | Infectious Disease | 3 (BT, FT, PR) | Y |
| 34 | Lunsumio | mosunetuzumab | 12-22 | Biologic | Roche | Refractory follicular lymphoma | Oncology (Others) | 4 (AA, BT, OD, PR) | Y |
| 35 | Xenoview | hyperpolarized Xe-129 | 12-22 | Small molecule | Polarean | MRI technique | Others (Medical Imaging) | 0 | Y |
| 36 | Briumvi | ublituximab | 12-28 | Biologic | TG Therapeutics | Multiple sclerosis | Central Nervous System | 0 | Y |
| 37 | NexoBrid | anaculase | 12-28 | Biologic | MediWound | Treatment of burns | Others (Burns) | 0 | Y |
*AA – Accelerated Approval, BT – Breakthrough Therapy, FT – Fast Track, OD – Orphan Drug, PR – Priority Review, VG – Priority Review Voucher Granted. See the ‘Approvals by FDA Special Designation’ section for more information.
FDA New Drug Approvals by the Numbers
Small Molecule vs. Biologics (2012-2022)
The FDA’s list of novel drug approvals can be broken down into either small molecules or biologics. Pharmaceutical companies will submit New Drug Applications (NDAs) for small molecules and Biologics License Applications (BLA) for biologics.
Though there is no official chemical distinction between the two, small molecules are classified as molecules produced through synthetic chemistry. In contrast, biologics are produced by living organisms (mammalian cells, bacteria, etc.) and subsequently isolated and purified.
This list does not include vaccines, gene therapies, or new indications for drugs previously approved.
Out of the 37 novel drug products approved by the FDA in 2022, 22 were small molecule drugs (59%), and 15 were biologic drugs (41%). The table and chart below compare the figures over the last 11 years (2012-2022).
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small molecules | 31 | 22 | 29 | 32 | 15 | 34 | 42 | 38 | 40 | 36 | 22 |
| Biologics | 6 | 3 | 11 | 12 | 7 | 12 | 17 | 10 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| Total | 37 | 25 | 40 | 44 | 22 | 46 | 59 | 48 | 53 | 50 | 37 |
| Biologics (%) | 16.2% | 12.0% | 27.5% | 27.3% | 31.8% | 26.1% | 28.8% | 20.8% | 24.5% | 28.0% | 40.5% |
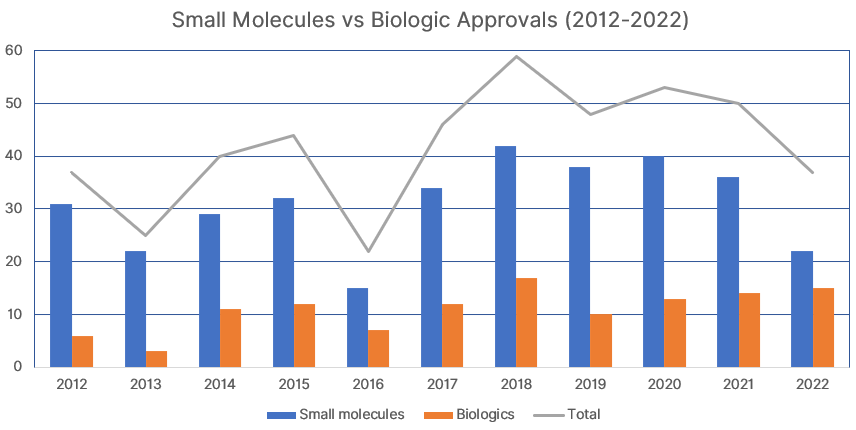
41% of drugs approved in 2022 were biologics, the highest ever proportion. The total of 37 drugs approved by the FDA in 2022 was the lowest since 2016, when there were 22 novel drug approvals.
2022 FDA Approvals by Drug Class
Out of the 37 drugs approved:
- 11 are oncology drugs for treating various cancers
- 7 are drugs for treating autoimmune diseases
- 4 are drugs to treat infectious diseases
- 4 are drugs to treat central nervous system (CNS) disorders
- 2 are ophthalmology drugs
- 1 is a cardiovascular drug
- 8 are uncategorized
First in Class Therapies
First-in-class therapies are drugs that work through a unique mechanism of action. They often replace or become the standard (first-line) treatment for their target patient group.
23 drugs approved in 2022 are considered first-in-class therapies (62% of the total).
Though ‘first-in-class’ is not a regulatory status, the FDA often places novel drugs under favorable designations (see below).
Approvals by FDA Special Designation
Accelerated Approval: 6 (16%)
Drugs may be granted accelerated approval status if they perform better than existing therapies but do not directly present this in primary endpoints (markers) during clinical trials. For such drugs, the pharmaceutical company can justify the suitability of intermediate endpoints and be granted accelerated approval.
Breakthrough Therapy: 10 (27%)
Breakthrough therapies are medicines that offer significant improvement over available therapies. They offer the drug developer more frequent meetings and communications with the FDA, including guidance and technical assistance from their experts.
Fast Track: 6 (16%)
A fast track designation is given to drugs that improve the outcomes for serious conditions with no prior effective standard treatments. This streamlines the review process, ensuring more frequent meetings and communication with the FDA.
Orphan Drug: 13 (35%)
As an incentive for pharmaceutical companies to develop ‘orphan’ therapies for diseases with less than 200,000 patients in the U.S., the FDA promises Orphan Drug designation and a reduced standard review time (10 months to 6 months) for such drugs.
An orphan drug designation also grants the manufacturer/patent holder an extended market exclusivity period, giving them more time to exclusively sell their drug before generics are allowed to enter the market.
Priority Review: 20 (54%)
A priority review designation reduces the time the FDA takes to perform a standard review (10 months to 6 months). It is granted to therapies that significantly improve the outcomes for a severe condition (diseases that are life-threatening or significantly impact daily function).
Priority Review Voucher Granted: 2 (5%)
Pharmaceutical companies that develop drugs approved for rare pediatric or tropical diseases can receive a priority review voucher. This voucher can be redeemed to assign the priority review designation to future drug candidates. It can also be sold to other manufacturers.
List of FDA New Drug Approvals 2022
The rest of the article reviews each drug product, including its indications, manufacturer, potential competitors, the commencement dates of each phase of clinical trials, and sales revenue (to be updated through 2023). You can read our comprehensive guide on the process and costs of drug development here.
Quviviq
Quviviq (daridorexant) is a small molecule drug (oral tablet) to treat adult patients with insomnia, characterized by sleep onset and sleep maintenance difficulties. It is a dual orexin receptor antagonist (DORA) developed by Idorsia Pharmaceuticals.
First in class: No.
Main Competitors: Merck’s Belsomra (suvorexant) was the first DORA, approved in 2014. Eisai’s Dayvigo (lemborexant) was approved in 2019.
Phase 1 trials: Jan 2020
Phase 2 trials: Jun 2022
Phase 3 trials: Jun 2018
Phase 4 trials: Oct 2022
Sales: Commercially available in the U.S. since May 2022. 10,000 monthly prescriptions for Quviviq, with net sales of US$2.4 million (September 2022).
Cibinqo
Cibinqo (abrocitinib) is a small molecule drug (oral tablet) to treat atopic dermatitis (eczema), skin inflammation caused by an immune response, in adults and adolescents 12 years and older. It is a selective Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) inhibitor developed by Pfizer.
First in class: No.
Main Competitors: Abbvie’s Rinvoq (upadacitinib) was the first JAK-1 inhibitor FDA-approved in 2019. Sanofi and Regeneron’s Dupixent for atopic dermatitis was approved in 2017.
Phase 1 trials: Apr 2013
Phase 2 trials: May 2016
Phase 3 trials: Nov 2017
Phase 4 trials: Nov 2022
Kimmtrak
Kimmtrak (tebentafusp-tebn) is a biologic peptide (intravitreal injection solution) to treat uveal (eye) melanoma, a rare form of cancer with a high fatality rate. Melanoma usually responds poorly to chemotherapy, which makes Kimmtrak the first proven standard treatment for uveal melanoma.
It is a human leukocyte antigen (HLA) specific T-cell engager developed by Immunocore. Kimmtrak is a bispecific molecule, which means it can target skin melanocytes (melanin-containing skin cells) and tumors derived from melanocytes on one end while recruiting T cells to its location on the other end to cause cell death.
Kimmtrak was developed by Immunocore.
First in class: Yes. Received breakthrough therapy, orphan drug and priority review designation by the FDA.
Phase 1 trials: Aug 2015
Phase 2 trials: Aug 2015
Phase 3 trials: Sep 2022
Pivotal Phase 2 trial: 378 patients with metastatic uveal melanoma that was HLA-A*0201 positive (~45% of cases) were treated with either Kimmtrak or another first-line melanoma therapy (dacarbazine, ipilimumab or pembrolizumab) as a control. Kimmtrak showed improved 1-year survival rates (73% vs. 59%) and overall survival duration (21.7 months vs. 16.0 months).
Vabysmo
Vabysmo (faricimab-svoa) is a biologic humanized bispecific antibody (intravitreal injection solution) to treat age-related wet macular degeneration and diabetic macular edema, where abnormal growth of blood vessels in the retina cause blurring and loss of vision.
It is a vascular endothelial growth factor (VAGF) and angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) inhibitor. Vabysmo was developed by Roche.
First in class: Yes. A priority review voucher was redeemed by Roche for the FDA review of this drug, shortening its review time.
Main Competitors: Regeneron’s Eyelea (aflibercept) is also a VEGF inhibitor for treating wet macular degeneration (approval in 2011), diabetic macular edema (approval in 2014) and all diabetes-related retinal damage (approval in 2019).
Phase 2 trials: Jun 2015
Phase 3 trials: Aug 2018
Phase 4 trials: Feb 2022
Enjaymo
Enjaymo (sutimlimab-jome) is a biologic monoclonal antibody (intravenous infusion) to treat cold agglutinin disease (CAD). This condition causes the body’s immune system to attack its own red blood cells at cold temperatures. It is a C1s enzyme inhibitor that prevents the autoimmune response and reduces the need for transfusion. Enjaymo was developed by Sanofi.
First in class: Yes. Received breakthrough therapy, orphan drug and priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Biogen’s Rituxan (rituximab) is the current first-line treatment for CAD, approved in 1997. Rituximab biosimilars are available after its patent expired in 2015.
Phase 3 trials: November 2017
Pyrukynd
Pyrukynd (mitapivat) is a small molecule drug (oral tablet). It is a pyruvate kinase (PK) activator that treats PK deficiency, a hereditary autosomal recessive disease that destroys red blood cells (hemolytic anemia). It was developed by Agios Pharmaceuticals.
First in class: Yes. Received orphan drug and priority review designation by the FDA.
Phase 1 trials: Jun 2019
Phase 2 trials: Nov 2020
Phase 3 trials: Feb 2021
Vonjo
Vonjo (pacritinib) is a small molecule drug (oral capsule) to treat cytopenic myelofibrosis (a rare form of bone marrow cancer). It is a Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) and FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) inhibitor, disrupting the signaling pathway that is associated with myelofibrosis. It was developed by CTI BioPharma.
First in class: Yes. Received accelerated approval, fast track, orphan drug and priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Novartis and Incyte Corp’s Jakavi/Jakafi (ruxolitinib) is a JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor for treating myelofibrosis, approved in 2011.
Phase 1 trials: May 2016
Phase 2 trials: Aug 2018
Phase 3 trials: May 2017
Ztalmy
Ztalmy (ganoxolone) is a small molecule drug (oral liquid suspension) to treat seizures due to cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) deficiency—a rare genetic disorder. The exact mechanism of action is unknown, but it is thought to normalize over-excited neurons by binding to GABA receptors. It was developed by Marinus Pharmaceuticals.
First in class: Yes. Received orphan drug and priority review designation by the FDA.
Phase 2 trials: Feb 2015
Phase 3 trials: Jun 2018
Pivotal Phase 3 trial: 101 CDKL5-deficient patients (2 years to 19 years old) showed a significant reduction in seizure frequency when given Ztalmy compared to placebo control (31% vs 7% reduction).
Ztalmy is currently undergoing phase 3 trials for pediatric patients (6 months to 2 years old) with CDKL5 deficiency.
Opdualag
Opdualag (nivolumab and relatlimab-rmbw) is a combination biologic therapy consisting of programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) inhibitor nivolumab and lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3) inhibitor relatlimab.
They are monoclonal antibodies administered by intravenous (IV) injection. It is indicated for stage 3 and 4 melanoma and was developed by Bristol Myers Squibb.
First in class: No. Received fast track, orphan drug and priority review designation by the FDA.
Phase 2 trials: Mar 2018
Phase 3 trials: Mar 2018
The pivotal phase 2/3 clinical trial showed the effectiveness of relatlimab + nivolumab vs. nivolumab alone for treating metastatic or unresectable melanoma, with increased median progression-free survival (10.1 months vs 4.6 months) as the major endpoint.
Pluvicto
Pluvicto (lutetium vipivotide tetraxetan) is a small molecule drug (intravenous injection) to treat prostate cancer. It was developed by Novartis.
Pluvicto is a radiopharmaceutical (containing the radioactive lutetium-177 isotope) that targets the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), a protein found on certain prostate cancer cells. Once at the location, it releases radiation through beta decay of the radioisotope that kills the tumor cells.
First in class: Yes. Received breakthrough therapy and priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Bayer’s Xofigo is another radiopharmaceutical (containing radium-223) that was approved for treating advanced prostate cancer in 2013; it is not currently used as a first-line treatment.
Phase 1 trials: Feb 2017
Phase 2 trials: Jan 2018
Phase 3 trials: Apr 2018
Vivjoa
Vivjoa (oteseconazole) is a small molecule drug (oral capsule) used to treat recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (chronic vaginal yeast infection). The antifungal works by inhibiting CYP51, preventing fungal growth and development. It was developed by Mycovia Pharmaceuticals.
First in class: No. Received priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: The generic drug fluconazole is the current first-line treatment for recurrent vaginal yeast infections. Oteseconazole is a useful alternative for fluconazole-resistant strains.
Phase 3 trials: Jun 2018
Camzyos
Camzyos (mavacamten) is a small molecule drug (oral capsule) used to treat hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (thickening of heart muscle). It works by inhibiting cardiac myosin (cells involved in muscle contraction) and was developed by Bristol Myers Squibb.
First in class: Yes.
Main Competitors: While there are no other cardiac myosin inhibitors, first-line treatment for obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy includes beta blockers and calcium channel blockers. Pfizer’s sodium channel blocker disopyramide is an alternative that has been used for this indication since 1982; it is also available as a generic drug today.
Phase 1 trials: Apr 2020
Phase 2 trials: Apr 2018
Phase 3 trials: Mar 2018
Sales: Reported cost of US$89,500 per year. Estimated annual sales of US$1 billion by 2025.
Voquezna
Voquezna (vonoprazan, amoxicillin and clarithromycin) is a co-package of vonoprazan oral tablets, amoxicillin oral capsules and clarithromycin oral tablets. They are small molecule antibiotics with different mechanisms of action designed to treat Helicobacter pylori infection. Voquezna was developed by Phathom Pharmaceuticals.
First in class: No. Received priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Vonoprazan is the only drug of the combination still under patent, produced as a single product Takecab. Takecab was approved for esophagitis in Japan in 2015, with U.S. FDA approval expected sometime in 2023. The patent holder for vonoprazan is Phathom’s parent company Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
Phase 3 trials: Dec 2019
Phase 4 trials: May 2021
Sales: Expected cost of US$812 per 14-day course.
Mounjaro
Mounjaro (tirzepatide) is a small molecule drug (weekly subcutaneous injection) to control blood sugar levels in adults with type 2 diabetes. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus cannot produce or use insulin normally, which results in high blood sugar levels.
Mounjaro activates glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), hormones that directly control insulin secretion. It was developed by Eli Lilly and Company.
First in class: Yes. Received priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy/Rybelsus/Ozempic are different doses of semaglutide for weekly subcutaneous injections. Semaglutide activates GLP-1 and was approved in 2017 for type 2 diabetes. Over 4 million prescriptions for Ozempic were filled in 2020.
Eli Lilly’s previous GLP-1 activator Trulicity (dulaglutide) was approved in 2014. Over 7 million prescriptions of Trulicity were filled in 2020 (US$5 billion in revenue). However, the patent for dulaglutide is set to expire in 2024.
With the GLP-1 market estimated to be worth US$11.3 billion in 2019 and growing to US$18.2 billion by 2027, Eli Lilly’s Mounjaro will have the time and patent protection period to reap the financial rewards.
Phase 1 trials: May 2016
Phase 2 trials: Apr 2017
Phase 3 trials: May 2019
Pivotal Phase 3 trial: Patients who took Mounjaro had lower blood sugar levels vs. placebo (~2% less) and higher weight loss vs. placebo (~18 pounds more). Subsequent trials also showed lower blood sugar levels vs. semaglutide (0.5% less) and higher weight loss vs. semaglutide (12 pounds more).
Sales: Expected cost of US$11,700 yearly.
In Q3 2022, Mounjaro more than doubled sales estimates of US$81 million, bringing Eli Lilly US$187 million in revenue. It looks well set to compete in diabetes and weight loss drug markets in the coming years, especially with manufacturing issues plaguing its competitors.
Vtama
Vtama (tapinarof) is a small molecule drug (topical cream) to treat plaque psoriasis, an autoimmune skin disease. It is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activator developed by Dermavant Sciences.
First in class: Yes.
Main Competitors: Although it is the first non-steroidal topical psoriasis treatment targeting AhR, there are similar treatments on the market. Acrutis Biotherapeutics’ Zoryve (roflumilast)—initially FDA-approved in 2011—received approval for higher dose regimens earlier this year. Zoryve treats plaque psoriasis by inhibiting phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) receptors.
Phase 2 trials: Aug 2019
Phase 3 trials: May 2019
Sales: Reported cost of US$1,325 per 60 g tube.
Amvuttra
Amvuttra (vutrisiran) is a small molecule drug (subcutaneous injection) for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis (hATTR). In hATTR, amyloid proteins are produced due to rare genetic mutations, causing blockage and disruption of normal organ function, especially the liver. Amvuttra is a gene-silencing drug developed by Alnylam Pharmaceuticals.
First in class: No. Received fast track and orphan drug designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Amvuttra is a synthetic small interfering RNA (siRNA) designed to prevent transthyretin (TTR) gene expression. Alynlam Pharmaceutical’s previous drug Onpattro (patisiran) was the first siRNA therapy approved in 2018, also targeting the TTR gene.
However, Amvuttra is administered by 3-monthly subcutaneous injections, while Onpattro is administered by 3-weekly intravenous infusions. This means Amvuttra is more convenient and less time-consuming to administer.
Phase 3 trials: Nov 2018
Sales: Expected cost of US$453,500 yearly.
Xenpozyme
Xenpozyme (olipudase alfa) is a biologic enzyme replacement drug (intravenous injection) to treat acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD), a genetic disorder that causes sphingomyelin buildup in cells, leading to improper organ function.
ASMD is estimated to affect 1200 people worldwide. Xenpozyme was developed by Sanofi.
First in class: Yes. Received breakthrough therapy, fast track, orphan drug and priority review designation by the FDA. Sanofi was also awarded a priority review voucher for future use.
Main Competitors: No other approved treatment for ASMD.
Phase 1 trials: Nov 2014
Phase 2 trials: Dec 2013
Phase 3 trials: Dec 2013
Sales: Expected cost of US$400,000 yearly.
Spevigo
Spevigo (spesolimab-sbzo) is a biologic monoclonal antibody (intravenous injection) therapy to treat generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), a rare form of psoriasis—an autoimmune disease that targets the skin. Spevigo inhibits the inflammatory interleukin-36 receptor and was developed by Boehringer Ingelheim.
First in class: Yes. Received breakthrough therapy and orphan drug designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: GPP is usually treated with corticosteroids and opioids. Spevigo is the first approved GPP-specific therapy.
Phase 1 trials: Aug 2018
Phase 2 trials: Dec 2018
Phase 3 trials: Jan 2022
Pivotal phase 3 trial: Spevigo showed complete clearance of skin pustules in 54% of patients with GPP vs. 6% clearance in the control (placebo) group.
Daxxify
Daxxify (daxibotulinumtoxinA-lanm) is a biologic cosmetic drug (intramuscular injection) to treat glabellar (frown) lines. It is an acetylcholine inhibitor that was developed by Revance Therapeutics.
First in class: No.
Main Competitors: Daxxify claims to have a better duration of action compared to traditional botulinum toxins (various manufacturers) used for cosmetic anti-wrinkle treatment.
Sales: The facial injectables market is worth US$3.2 billion.
Sotyktu
Sotyktu (deucravacitinib) is a small molecule drug (oral tablet) to treat plaque psoriasis, an autoimmune skin disease. It is a tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor developed by Bristol Myers Squibb.
First in class: Yes.
Main Competitors: Sotyktu’s exact mechanism of action is unknown, but other treatments for plaque psoriasis include Abbvie’s Humira (adalimumab) and other injectable biologics. Sotyktu’s oral route of administration may be more attractive to patients.
Phase 1 trials: Sep 2020
Phase 3 trials: Jul 2019
Rolvedon
Rolvedon (eflapegrastim) is a biologic drug (subcutaneous injection) to reduce the chance of infection in patients receiving myelosuppressive anti-cancer drugs. Patients who receive chemotherapy can suffer from neutropenia, low counts of white blood cells, suppressing a normal immune response.
Rolvedon is structurally similar to colony-stimulating factor 3, a growth hormone that promotes the growth of cells in the bone marrow. It was developed by Spectrum Pharmaceuticals.
First in class: No.
Main Competitors: Pegfilgrastim and filgrastim also treat neutropenia by promoting white blood cell growth. They are available as biosimilars (generics) under various brands worldwide.
Phase 1 trials: Dec 2009
Phase 2 trials: Nov 2012
Phase 3 trials: Dec 2015
Terlivaz
Terlivaz (terlipressin) is a small molecule drug (intravenous injection) for improving kidney function in patients with liver disease or liver failure. Termed hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), the condition is a complication of late-stage liver disease and is usually fatal.
Terlivaz increases blood flow to the kidneys by preventing vasopressin receptors (that cause blood vessel constriction) from activating. It was developed by Mallinckrodt.

First in class: Yes. Received fast track, orphan drug and priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Other vasoconstrictor therapies include adrenaline (epinephrine), though the effects are systemic (entire body) rather than kidney-targeted. Midodrine is another generic that increases systemic blood flow and is currently the first-line treatment for HRS.
Phase 1 trials: Jun 2011
Phase 2 trials: Jun 2011
Phase 3 trials: May 2016
Pivotal Phase 3 trial: Patients who took Terlivaz had improved kidney function vs. placebo (29% vs 16%) after 14 days or less.
Elucirem
Elucirem (gadopiclenol) is a small molecule contrast agent (intravenous injection) used in MRI. It contains gadolinium metal ions and helps to visualize abnormal vascular lesions (tissues with malformed blood vessels). It was developed by Guerbet.
First in class: No. Received priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Several gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents like gadopentetic acid exist and are available as generics. While they are FDA-approved for use in the U.S., many of them are banned in the EU due to their linear structure (there are worries that the gadolinium ion can escape and impair brain function).
Elucirem has a macrocyclic structure, holding the gadolinium ion more strongly within its structure. The contrast agent is currently under review by the European Medicines Agency for approval in the EU.
Phase 1 trials: Jul 2018
Phase 3 trials: Jun 2019
Omlonti
Omlonti (omidenepag isopropyl ophthalmic solution) is a small molecule drug (ophthalmic solution—eye drops) for reducing intraocular pressure in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It is a prostaglandin E2 (EP2) receptor activator and was developed by Santen Pharmaceutical.
First in class: Yes.
Main Competitors: Other prostaglandin analogs (latanoprost), beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists (betaxolol), alpha-adrenergic receptor agonists (brimonidine) and muscarinic receptor agonists (pilocarpine) are currently used to reduce intraocular pressure. Many generic versions of these are available.
Relyvrio
Relyvrio (sodium phenylbutyrate/taurursodiol) is a small molecule drug (oral suspension) for treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). It was developed by Amylyx Pharmaceuticals.
First in class: Yes. Received orphan drug and priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: There is currently no cure for ALS. Current treatments include the generic drug riluzole which increases survival in ALS patients. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma’s Radicava (edaravone) has shown evidence for slowing ALS progression.
Phase 1 trials: August 2021
Phase 2 trials: Apr 2017
Phase 3 trials: Ongoing
Pivotal phase 2 trial: In a trial of 137 adult patients with ALS, Relyvrio slowed the rate of symptom progression and increased patient survival compared to the placebo.
An independent advisory panel voted against Relyvrio’s approval in March 2022, citing too small of a phase 3 study. However, this was later reversed upon appeal.
Sales: There are an estimated 20,000 patients with ALS in the U.S.
Lytgobi
Lytgobi (futibatinib) is a small molecule drug (oral tablet) for treating cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer). It is a fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor, a receptor that—when activated—helps tumor cells survive and grow. Lytgobi was developed by Taiho Oncology.
First in class: No. Received accelerated approval, breakthrough therapy, orphan drug and priority review designations by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Cholangiocarcinoma is rare, with about 8,000 diagnoses in the U.S. each year. Of these, only around 250 patients fall under Lytgobi’s indication for FGFR inhibition. Other FGFR inhibitors approved for bile duct cancer include Incyte’s Pemazyre (approved in 2020) and QED Therapeutic’s Truseltiq (approved in 2021).
Phase 1 trials: Feb 2014
Phase 2 trials: Feb 2014
Imjudo
Imjudo (tremelimumab) is a biologic, fully human monoclonal antibody (intravenous injection) to treat hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). It is an immune checkpoint blocker that targets cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA4). This releases cytotoxic T-lymphocytes that promote an immune response against the tumor cells.
Imjudo was developed by AstraZeneca. It is indicated for use with AstraZeneca’s other checkpoint blocker Imfinzi (durvalumab), which was approved in 2017.
First in class: No.
Main Competitors: Bristol Myers Squibb’s Yervoy (ipilimumab) is also a CTLA4 blocker used to treat liver cancer, approved in 2011. The protein kinase inhibitor sorafenib (available as a biosimilar) is also a treatment option for liver cancer.
Phase 1 trials: May 2013
Phase 2 trials: Aug 2015
Phase 3 trials: Oct 2017
Tecvayli
Tecvayli (teclistamab-cqyv) is a biologic human monoclonal antibody (subcutaneous injection) for treatment-resistant multiple myeloma (blood plasma cancer). It works by engaging T cells to the sites of tumors expressing B-cell maturation antigens (BMCA), destroying them.
Tecvayli is considered a fifth-line treatment for those who have received four prior chemotherapies with other mechanisms of action. It was developed by Johnson & Johnson.
First in class: Yes. Received accelerated approval, breakthrough therapy, orphan drug and priority review designations by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Bristol Myers Squibb’s Abecma (approved in 2021) and Johnson & Johnson’s own Carvykti (approved in 2022) also target the BCMA protein on myeloma tumor cells. However, they are CAR-T therapies that require harvesting of patient T cells, while Tecvayli can be administered as manufactured.
Phase 1 trials: May 2017
Phase 2 trials: Sep 2020
Sales: Price range of US$355,000 to US$395,000 for a 9 to 10-month course.
Elahere
Elahere (mirvetuximab soravtansine-gynx) is a unique biologic-small molecule drug combination (intravenous injection) to treat ovarian cancer. The biologic monoclonal antibody portion targets the folate receptor alpha (FRα) in tumor cells and the small molecule is an anti-tubulin agent that disrupts microtubules during cell division. Elahere was developed by ImmunoGen.
First in class: Yes. Received accelerated approval and priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: First-line chemotherapy treatment for late-stage (advanced) ovarian cancer is taxane and/or platinum therapy. Roche’s Avastin (bevacizumab, approved in 2004) also targets advanced ovarian cancer, although Elahere can be taken by patients previously treated with it. AstraZeneca’s Lynparza (olaparib, approved in 2014) is another alternative. Elahere is the first drug specifically targeting advanced ovarian cancer approved since Lynparza.
Phase 1 trials: Jun 2012
Phase 2 trials: Nov 2015
Phase 3 trials: Dec 2015
Sales: The cost for each round of treatment is reported to be between US$18,500 and US$25,000.
Tzield
Tzield (teplizumab-mzwv) is a biologic monoclonal antibody (intravenous injection) to slow the progression of type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, where the immune system destroys the cells that produce insulin. Usually diagnosed in children, patients with type 1 diabetes require regular insulin injections to control their blood glucose levels.
Tzield deactivates the immune response against these insulin-producing cells, slowing the progression of type 1 diabetes. Tzield was developed by Provention Bio.
First in class: Yes. Received breakthrough therapy and priority review designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: There is no other treatment for type 1 diabetes prevention. This first-line option can benefit many; there are 1.9 million people with type 1 diabetes in the U.S. alone. However, screening for diabetes before symptoms appear is a challenge. Tzield works best while patients display no to mild symptoms as it slows the progression of the disease.
Pivotal phase 2 trial: Tzield is administered over 14 consecutive days and was shown to slow the progression of stage 2 to stage 3 (50 months vs. 25 months in placebo), among other endpoints.
Sales: Reported to cost US$193,000 for the 14-day treatment.
Rezlidhia
Rezlidhia (olutasidenib) is a small molecule (oral capsule) for treating certain cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). It is a mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) inhibitor that was developed by Rigel Pharmaceuticals.
First in class: No.
Main Competitors: Servier’s Tibsovo (ivosidenib), another IDH1 enzyme inhibitor for treating AML, was approved in 2018. Agios Pharmaceuticals’ Enasidenib (idhifa) is an IDH2 inhibitor, approved in 2017, also for treating AML.
Phase 1 trials: Mar 2016
Phase 2 trials: Mar 2016
Krazati
Krazati (adagrasib) is a small molecule (oral tablet) used as a second-line treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It is an inhibitor of the RAS GTPase family of enzymes found in mutant subtypes of NSCLC. Krazati was developed by Mirati Therapeutics.
First in class: No. Received accelerated approval, breakthrough therapy, fast track and orphan drug designation by the FDA.
Main Competitors: Amgen’s Lumakras (sotorasib) is another RAS GTPase inhibitor for treating NSCLC; it was approved in 2021.
Phase 1 trials: Dec 2018
Phase 2 trials: Dec 2018
Sales: Reported to cost US$19,750 for a 30-day supply (twice daily regimen).
Sunlenca
Sunlenca (lenacapavir) is a small molecule (subcutaneous injection) therapy administered 6-monthly to patients with HIV. It binds to the outer shell of HIV viruses, preventing its breakdown and the release of viral RNA into the host cell. Sunlenca was developed by Gilead Sciences.
First in class: Yes. Received breakthrough therapy, fast track and priority review designation by the FDA.
Main competitors: Although Sunlenca has shown evidence of being more potent than existing HIV treatments, it is meant to be used as a backup option in HIV patients who have exhausted other more established antiretroviral treatment options.
Phase 1 trials: Nov 2018
Phase 2 trials: Nov 2019
Phase 3 trials: Nov 2019
Lunsumio
Lunsumio (mosunetuzumab) is a biologic (intravenous injection) therapy for the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL) that has relapsed after prior treatment. It is a bispecific monoclonal antibody that targets CD-20 receptors on tumor cells and CD-3 receptors on human T-cells. Lunsumio was developed by Roche.
First in class: Yes. Received accelerated approval, breakthrough therapy, orphan drug and priority review designations by the FDA.
Main competitors: Novartis’ Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel) is an antibody that targets the CD-19 receptor approved in 2017 for treating relapsed FL. However, Kymriah cannot be directly administered, requiring a gene therapy step before the patient can start treatment.
Phase 1 trials: Jul 2015
Phase 2 trials Jul 2015
Xenoview
Xenoview (hyperpolarized Xe-129) is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique that replaces traditional helium with xenon. This improves the signal intensity, making it possible to visualize less dense structures like the lungs. Xenoview was developed by Polarean.
First in class: Yes
Main competitors: Xe-129 MRI has been studied since 2013, with full clinical trial data available, yet concerns over its anesthetic properties have delayed the technique’s FDA approval. Currently, pulmonary imaging is done using X-ray CT scans, although this does not provide information in as much detail.
Briumvi
Briumvi (ublituximab) is a biologic (intravenous injection) therapy for treating multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune condition that targets the brain and spinal cord. Briumvi is a monoclonal antibody that targets the CD20 receptor on abnormal B cells, leading to their destruction. It was developed by TG Therapeutics.
First in class: No
Main competitors: Roche’s Ocrevus (ocrelizumab) is another MS treatment that targets B cells through the CD20 receptor. It was approved by the FDA in 2017.
Phase 1 trials: Jul 2012
Phase 2 trials: Apr 2016
Phase 3 trials: Sep 2017
Sales: Reported to cost US$30,000 per year.
NexoBrid
NexoBrid (anacaulase) is a biologic (topical gel) therapy for treating severe burns. It is a sterile enzyme mixture that non-surgically removes eschar (dead tissues) without affecting viable tissue in the surrounding area. NexoBrid was developed by biopharmaceutical company MediWound.
First in class: Yes
Phase 3 trials: Oct 2014
This list of 2022 FDA new drug approvals will continue to be updated by our editors through 2023. Bookmark this page to receive the latest information and sales figures as they become available!
About the Author

Sean is a consultant for clients in the pharmaceutical industry and is an associate lecturer at La Trobe University, where unfortunate undergrads are subject to his ramblings on chemistry and pharmacology.